High Chlorine Low pH: Why is it Important to Fix?
Table of Contents
What Happens If Chlorine Is High and pH Is Low?
High chlorine low pH means that the pool water is more acidic than it should be. Swimmers will get skin and eye irritation. Metallic parts of the pool equipment, such as pumps and filters will corrode and the life expectancy of plaster pool walls will reduce.
This article is invaluable if your primary concern is high chlorine and low pH in your pool. But why not equip yourself with an interactive tool that is like a Swiss knife for pool water chemistry?
It seems that as a pool owner you are always trying to balance the pool chemicals. The entire process can be quite overwhelming if you are new to this game.
There are at least 5 key measurements that must be maintained within a recommended range. So, what happens if chlorine and pH is low in your pool?
Chlorine is, arguably, the most important pool chemical. Its role is to keep the water disinfected and sanitized. It does this by killing the pathogens that can cause diseases. A chlorine level of 2-4 ppm is sufficient to get the job done.
Chlorine reacts with the pool water to form a weak acid called Hypochlorous Acid (HOCL) which sanitizes & disinfects by killing the viruses, germs, bacteria & algae.
The acid penetrates the cell walls of the pathogens and makes the cell’s protein backbone dysfunctional.

High chlorine will have an impact on the cell walls of human skin and eyes resulting in irritation and redness.
On the other hand, pH is not a chemical but a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of water. A pH of 7.0 is neutral; lower readings are a measure of acidity and higher readings are a measure of alkalinity.
In pool chemistry high chlorine and low pH are undesirable as the pool water is too acidic. A high chlorine low pH leads to an unpleasant swimming experience and corrosion of pool equipment and walls.
How Does pH Affect Chlorine Effectiveness?
The pH of pool water and chlorine effectiveness are related. The relationship is not linear but lower pH increases chlorine effectiveness and higher pH reduces chlorine effectiveness.
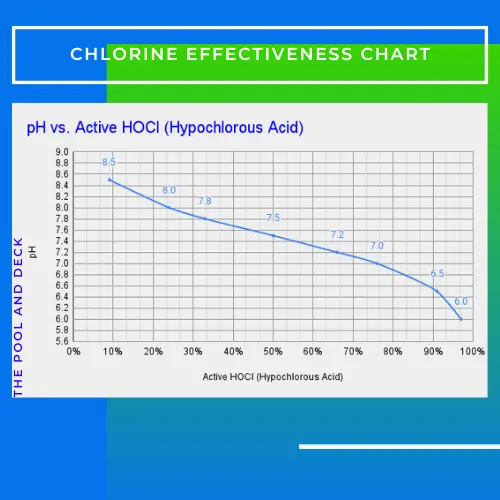
It would seem that it is best to have pH Level below 6.5 so that you can have chlorine effectiveness of 90% or more. However, this is not practical as the pool water will be too acidic for a pleasant swim. Moreover, the maintenance cost of your pool will shoot up!
On the other hand, having high pH levels anyway is not good as chlorine would hardly be effective. Your pool will be infested with harmful pathogens and slimy algae. The pool will be both unsafe and unappealing!
What is the Ideal pH Level for Chlorine?
So that brings us to the question of, “What is the ideal pH level for Chlorine?
The sweet spot is to have a pH level of between 7.4 and 7.6. Chlorine effectiveness will be around 50%. The pH level is very mildly alkaline and does not irritate the human skin or eyes. At the same time chlorine effectiveness is good enough to eliminate the pathogens.
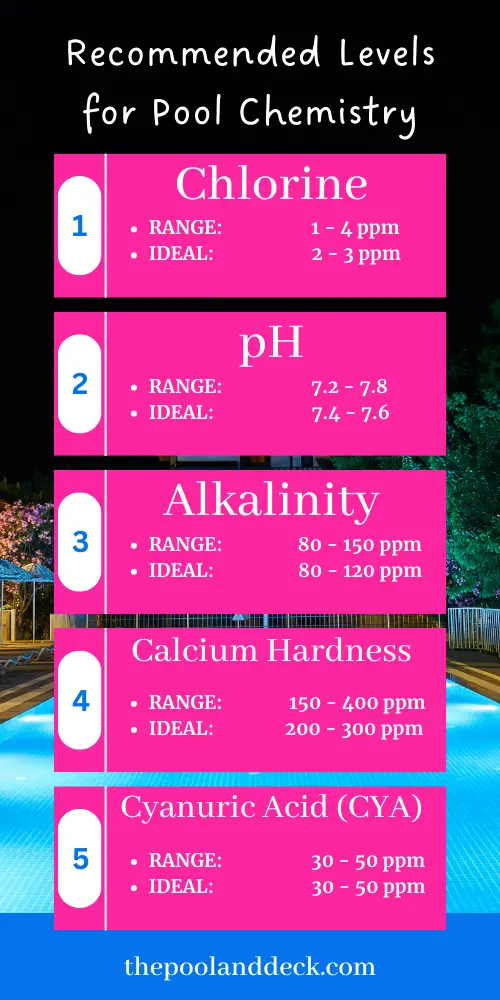
Here is an infographic on the recommended levels for pool chemistry.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Click on the image below to reach the page with all the Necessary Pool Chemicals.
Does Adding Chlorine Raise or Lower pH?
There are 4 different types of chlorine that may be used in a swimming pool. The impact they have on the pH level is as under:
Trichlor
Trichlor tablets are extremely popular for keeping a pool sanitized. They come as 1” or 3” tablets and can be inserted in floaters or the pool skimmers. Trichlor tablets have a pH level of around 3, so they will lower the pH of your pool water.
Dichlor
Dichlor comes in powder or granular form and is often favored as a shock. It is convenient to mix with water and broadcast the solution along the pool edge. It can simply be sprinkled as well.
Dichlor is very slightly acidic with a pH level of 6.5. It is reasonably close to neutral, and will have little effect on the pH level of your pool.
Cal Hypo
Calcium hypochlorite is highly alkaline with a pH of around 12, so it will raise the pH level of the water, as well as increase the calcium hardness level. Cal Hypo is an ideal shock for your pool as it does not have any cyanuric acid (CYA).
Liquid Chlorine
Liquid chlorine has an even higher pH level of around 13, so it will also increase the pH of your water.
The impact of chlorine addition on pH levels of your pool are only temporary. In any case the overall impact, over a period of time, is quite low as the ideal chlorine level of a pool should be in the 2 – 4 ppm range.
How To Stabilize pH Levels in a Pool?
While pH levels affect chlorine effectiveness, pH levels are closely related to alkalinity levels. To maintain a stable pH level in a pool and keep the pool chlorine working at optimum levels you need to monitor alkalinity levels of your pool as well.
The recommended alkalinity level range for a pool is between 80 to 120 ppm. Get the alkalinity level right and chances are the pH will stay within the recommended range and not swing wildly.
NOTE: Quite often it is assumed that pool alkalinity and pool pH mean the same thing. In fact they are different, even though they are closely related.
Total alkalinity refers to the amount of dissolved alkalis in your pool, measured in parts per million. Whereas the pH of pool water is a measure of the acidity on a scale from 0 to 14.
Neutral water has a pH of 7.0. Highly alkaline water has a high pH while highly acidic water has a low pH.
You can increase the pH of your pool by adding Sodium Carbonate (Soda Ash) or pH Up.
On the other hand you can lower the pH of your pool by adding Muriatic Acid or pH Down.
For more information check out my Pool Chemistry for Beginners: With 5 Super Helpful Cheat Sheets!
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and helpful.








