Do Phosphates Consume Chlorine? (It Is Important To Know!)
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Table of Contents
Do Phosphates Consume Chlorine?
With a pool in your backyard, you have had to learn about pool chemistry. You already know a fair bit about chlorine, cyanuric acid, algaecides, clarifiers and stuff like that.
But what about “phosphates”? You may have heard a few disturbing facts, but do phosphates consume chlorine?
This article is invaluable if your primary concern is regarding phosphates consuming chlorine. But why not equip yourself with an interactive tool that is like a Swiss knife for pool water chemistry?
Phosphates do not consume chlorine directly, through any chemical reaction. Phosphates are micronutrients for microorganisms, especially algae.
An increase in phosphates in your pool will promote algae growth, which increases the chlorine demand. Phosphates, therefore, consume chlorine indirectly.
Why do Phosphates NOT React with Chlorine?
The phosphate ( PO4^3-) ion has no affinity for the hypochlorite (OCl-) ion, as both are anions, that is negatively charged.
Phosphate, also known as orthophosphate, a negatively charged ion, is a chemical derivative of phosphoric acid. The chemical formula is
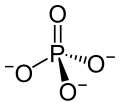
Phosphoric acid when dissolved in water gives a hydronium cation (positively charged) and a phosphate anion (negatively charged). The chemical equation is:
H3PO4 + 3H2O <=> 3H3O^+ + PO4^3-
Free Active Chlorine (FAC) or Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) co-exists in the water along with a hydrogen cation (positively charged) and a Hypochlorite anion (negatively charged). The chemical equation is:
HOCL <=> H+ + OCl-
As both phosphate and hypochlorite ions are anions (negatively charged), they are not attracted to each other.
The level of phosphate in the pool does not decrease when a pool is shocked. This is clear evidence that phosphate does not react with or consume HOCl, which is Free Active Chlorine (FAC).

What Raises Phosphate Levels In Pools?
Phosphates enter your swimming pool from the water used to fill the pool, surrounding environment and even some pool chemicals.
Phosphorus and its compounds as phosphates exist in nature in rocks & soil and in living & decaying plants & animals. Man-made fertilizers are also rich in phosphates.
Phosphates can enter your pool through the water supply. Well water has natural phosphate from the soil while tap water has phosphates added artificially to reduce scaling.
Phosphates can also be blown in due to rain & wind storms. Yard debris, such as leaves, grass clippings, etc., is also a phosphate source for swimming pools.
Even some pool chemicals, such as “sequestering agents” are phosphate-based. So if you are using a phosphate-based pool chemical, knowingly or unknowingly, you are adding phosphates to your pool.
What Does High Phosphate Do To Your Pool?
Phosphates are food for algae. High phosphate levels in your pool can accelerate the growth of algae and may even turn your blue pool, green.
Algae is a microorganism from the plant kingdom. LIVESCIENCE defines algae as
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that have the ability to conduct photosynthesis.
LIVESCIENCE
Phosphates, along with Nitrates, are micronutrients for algae. Algae can double in 3-8 hours if they have water, micronutrients, and sunlight for photosynthesis.
High phosphate levels increase the reproduction rate of algae and put a high demand on the Free Available Chlorine (FAC). At this stage, it is basically a war between chlorine and algae.
The phosphates are helping algae grow fast. If the “reproduction rate” of algae exceeds the “kill rate” of chlorine, you run the risk of your pool being overtaken by an “algae bloom“.
So, indirectly and through the algae, high phosphates consume chlorine.
The only way to combat this situation is to shock your pool in quick succession, till the “kill rate” of the chlorine surpasses the “reproduction rate” of algae.
Is It Safe To Swim In A Pool With High Phosphates?
Generally speaking, it is quite safe to swim in a pool with high phosphates.
Phosphates, by themselves, are not harmful to human health as long as they are within reasonable levels. The phosphate level has to exceed 1000 ppb (that is, parts per billion) before it becomes a health concern. Typically a pool may have a phosphate level of 100 ppb .
However, you should be wary of swimming in a pool that has poor visibility, due to high algae growth. Do not swim in a pool if the pool bottom is not visible. This is a very basic safety rule to avoid pool accidents.
High phosphate levels in your pool can lead to an increase in algae. Your pool may develop a greenish cloudy tinge. The pool may turn cloudy white after shocking, because of all the dead algae floating around. To clear the pool use a pool flocculant and then vacuum the pool floor.
It is important to make sure that the phosphate level in your pool does not go too high. Keeping phosphate levels in check will reduce the chances of unexpected algae growth and make your pool chlorination efforts more effective.
How To Bring Phosphates Down In A Pool?
Though phosphates are an important element of the pool chemistry, you do not need to check the phosphate level every week. As a matter of fact, most pool test kits do not even have a phosphate level tester.
You can test the phosphate level, either by buying a special phosphate testing kit or by taking a sample of the pool water to the local store for pool supplies. Testing phosphate level once every six months is good enough.
There are homemade phosphate remover for pools, such as vinegar or baking soda, but their efficacy is questionable.
A pool chemical called “Phosfree” will remove phosphates from your pool. In case the calcium levels in your pool are low then adding calcium increasers will get the calcium level up and the phosphate level down.
To avoid buildup of phosphates in your pool,
- Skim the surface of your pool regularly, to remove floating debris, such as leaves. Definitely do this after a storm.
- Brush the sides and bottom of your pool regularly.
- Vacuum your pool often.
Can You Put Too Much Phosphate Remover In A Pool?
High phosphates do indirectly consume the pool chlorine and can lead to increase in algal activity. But there is no need to keep pouring phosphate remover in your pool, every now and then.
You should not use a phosphate reducer unless the phosphate level exceeds the 1000 ppb mark. Phosphate reducers can interfere with the performance of other pool chemicals, particularly sequestering agents.
Sequestering agents, used to remove metals, like copper & iron, are phosphate based. A phosphate remover will neutralize the sequestering agent.
For more information on Pool Chlorine Types refer to my post Complete Guide To Pool Chlorine Types. (What Is The Best?).
Recommended Swimming Pool Chemicals
Best Phosphate Remover
Natural Chemistry Pool Perfect + Phosfree can be used regularly, if you are not using sequestering agents. It removes phosphates, cleans water lines and filters and reduces surface oils and other contaminants.
Natural Chemistry Pool Perfect + Phosfree
Natural Chemistry Pool Perfect + Phosfree
- Add weekly to maintain near zero phosphate levels
- Cleans waterline and filer
- SMARTZyme technology reduces frequency of filter cleaning and scrubbing scum lines
Best Liquid CYA Free Pool Shock
Champion Liquid Chlorine (Sodium Hypochlorite) Pool Shock (12.5%) is easy-to-use, fast, and effective. This Pool Shock does not have Cyanuric Acid (CYA-stabilizer) and will not result in build-up of scale. Order from Amazon using the link below:
Liquid Chlorine Pool Shock (Case – 4 Gallons) – 12.5% Sodium Hypochlorite
Best Cal-Hypo Pool Shock
Calcium Hypochlorite Cal-Chlor chlorine granules, from In The Swim, provide 68% available chlorine for hard-hitting immediate results! Non-stabilized formula is ideal for super shocking or everyday use as it does not contain any Cyanuric Acid (CYA). Order from Amazon using the link below:
In The Swim Calcium Hypochlorite Chlorine Granular Pool Shock
Best Trichlor Tablets
Rx Clear 3″ Stabilized Chlorine tablets are 99% Trichlor with added benefits of containing bactericide, algaecide, and disinfectant. It is slow dissolving with 90% available chlorine. The dosage is 1 tablet per 10,000 gallons of pool water which lasts for up to one week. Order from Amazon using the link below:
Rx Clear 3-Inch Water Soluble Chlorine Tabs
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and helpful.








