pH Increaser vs Alkalinity Increaser: What is Best When?
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Table of Contents
Is pH Increaser the Same as Alkalinity Increaser?
pH Increaser vs Alkalinity Increaser and what is more important can be a bit confusing. They are certainly not the same thing, because pH and Total Alkalinity (TA) are not the same thing.

You need the pH Increaser to increase pH and the Alkalinity Increaser to increase pool alkalinity. However, as pH and alkalinity are inter-related a pH Increaser will increase alkalinity too and an alkalinity increaser will increase pool pH too!
Both pH and alkalinity are important for variables in pool water chemistry. Both have to be kept within an ideal range.
In case the pH and / or alkalinity drop below the minimum recommended level, then you must add either a pH Increaser or the alkalinity increaser or sometimes both to get the levels back within range.
Key Takeaways
- pH Increaser raises pH but also slightly increases alkalinity.
- Alkalinity Increaser raises TA but has a minimal effect on pH.
- Ideal pH range is 7.2–7.8; ideal TA range is 80–120 ppm.
- Low pH causes corrosion, irritation, and equipment damage.
- Low TA leads to unstable pH, affecting water balance.
- TA stabilizes pH and buffers against rapid fluctuations.
- Regular testing ensures balanced and safe pool water.
Effect of Low pH in Pool
If swimming in your pool is irritating your eyes and skin then chances are that the pH of the pool water has dropped below 7.2. The functioning and longevity of the pool equipment and pool surfaces will be reduced due to corrosion, etching and pitting.
If the water test shows a pH of less than 7.2 then you need to add a pH Increaser to your pool. A pH Increaser is also sold as a pH Up or a pH Plus. They all have the same effect as the active ingredient in them is sodium carbonate (soda ash).
Effect of Low Alkalinity in Pool
A drop in the alkalinity levels of your pool has quite the same effect as low pH. In addition low alkalinity causes the pH of your pool to fluctuate wildly. It is quite difficult to stabilize pH at low alkalinity levels.
If the water test shows a Total Alkalinity (TA) of less than 80 ppm then you need to add an Alkalinity Increaser to your pool. An Alkalinity Increaser is also sold as a Alkalinity Up or a Alkalinity Plus. They all have the same effect as the active ingredient in them is sodium bicarbonate (baking soda).
In essence you will often need to use both an Alkalinity Increaser and a pH Increaser. You will also need to use the Alkalinity Increaser first as it is a pH buffer and will make it easier to get the pH in range.
Click on the image below to reach the page with all the Necessary Pool Chemicals.
Difference Between pH and Alkalinity
The difference between pH and alkalinity, in a nutshell, is that
pH refers to how acidic or basic your pool water is, while alkalinity is a measure of the water’s ability to resist changes in pH.
pH is a measure of the acidity or the alkalinity of the pool water. Total Alkalinity (TA) is a measure of the amount of alkaline particles dissolved in the water. The alkalinity of water is its ability to neutralize acids.
Alkalinity therefore acts, and is known as a pH buffer!
How is pH Measured?
A logarithmic scale from 0 to 14 is used to measure pH. Distilled water at a pH of 7 is considered neutral. A pH level below 7 indicates that your pool water is acidic, while a pH level above 7 indicates that your water is alkaline.
Note that the scale is logarithmic. So water with a pH of 6 is not just a bit more acidic than water with a pH of 7, considered neutral. It is 10X more acidic!
Maintaining proper pH level is crucial. In case pH is low and your pool water is too acidic, it can cause eye and skin irritation, damage your pool equipment, and even corrode your pool walls and floor.
On the other hand, if pH is high and your pool water is too alkaline, it can cause calcium deposits on your pool surfaces, reduce the effectiveness of chlorine, and make your water cloudy.
How is Total Alkalinity (TA) Measured?
Total Alkalinity is a measure of the ability of pool water to resist changes in pH. It is a measure of the quantity of alkaline particles in the water and is measured in parts per million (ppm).
Total Alkalinity acts as a buffer, helping to stabilize pH levels and prevent rapid changes.
Low Total Alkalinity can cause the pH to fluctuate rapidly, which can damage your pool equipment and surfaces. On the other hand, if your alkalinity is too high, it can make it difficult to adjust the pH level, which can cause cloudy water and reduce the effectiveness of chlorine.
There are 5 vital pool chemistry measurements that you must take on a regular basis. Total Alkalinity (TA) and pH are 2 of those 5. Check out the infographic below. It is a helpful ready reckoner that you can save on your phone.
The ideal range for total alkalinity (TA) is between 80 and 120 ppm while the ideal pH level for your pool water is between 7.2 and 7.8. Regular testing and proper chemical adjustments will help ensure that your pool water remains crystal clear, safe, and enjoyable for everyone to swim in.
Can I Use Alkalinity Increaser to Raise pH?
An Alkalinity Increaser will also increase pH. However, the increase in pH is very small in comparison to the increase in alkalinity. So, your Total Alkalinity (TA) will go beyond the range much before you can get any meaningful increase in pH. In short, using Alkalinity Increaser to raise pH is not practical.
I have prepared the infographic below based on data from the Pool Calculator website.
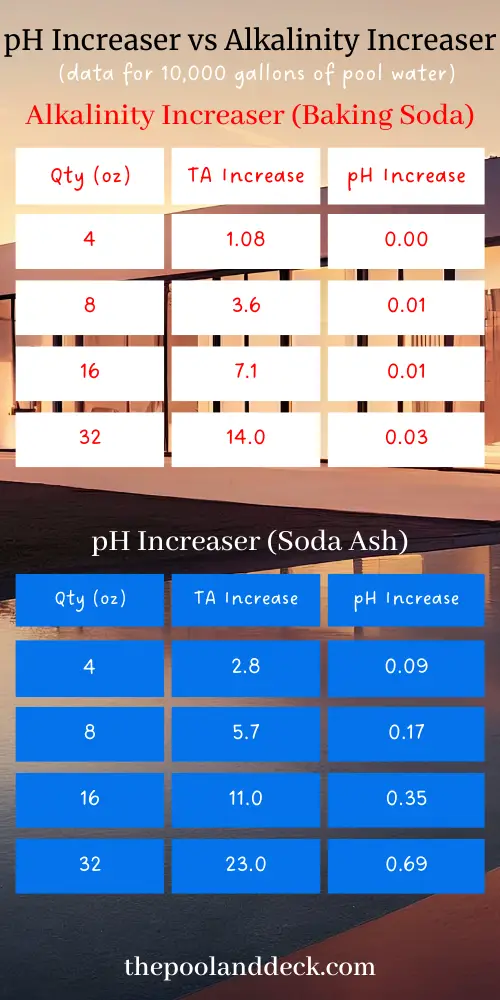
So as you can see the impact of adding an alkalinity increaser to your pool has quite a small impact on the pH increase,
Let us say the test results of your pool water show an alkalinity of 70 ppm and a pH of 7.0. Both need to be increased.
To get an increase of 0.3 in pH, in a 10,000 gallon pool with just an Alkalinity Increaser would be near impossible. Adding as much as 4 lbs of baking soda (Alkalinity Increaser) will barely move the pH but alkalinity would already have hit nearly 100 ppm.
So the right approach would be to add 4 lbs of baking soda, let it circulate and test the pool water once again after 6 – 8 hours. Chances are that now the pH stands at 7.1 and total alkalinity (TA) stands at 100 ppm.
At this point if you add 1 lb of soda ash (pH Increaser) the likely final result is pH at 7.3 – 7.4 and total alkalinity (TA) at 110 ppm.
You can also use my Pool Baking Soda Calculator to determine the dosage for your pool.
Bottom Line
The bottom line is that the pH Increaser vs Alkalinity Increaser debate is meaningless. Each has a role to play in maintaining the water chemistry of your pool within recommended levels.
Quite often, both pH and Total Alkalinity (TA) of a pool are low. In such situations you have to add an Alkalinity Increaser first to get it up and act as a pH buffer. This needs to be followed with the addition of a pH Increaser.
With the right quantities and with one or two iterations you will be able to get both pH and Total Alkalinity (TA) in line.
Recommended Products:
For more information check out my Pool Chemistry for Beginners: With 5 Super Helpful Cheat Sheets!
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and helpful.







